Stop Catastrophic Cyber Failure: Step #2– Align Security Controls to Reduce Risk
In part three of the “Threat Based Security Model” series, we’ll create policies based on our risks and then align our security controls to them.
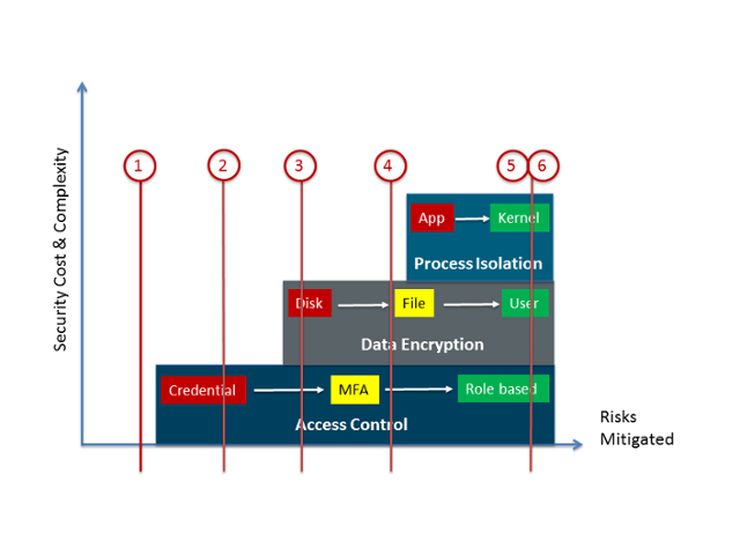
Within each layer, security controls are prioritized in increasing strength, from left to right, as shown in the diagram above.
In the data encryption layer, there exists a wide range of encryption types, ranging from disk-based encryption being the least secure. File-based encryption is the next level up, providing an additional layer of security. Finally, data files only readable by a specific user are the strongest – especially when the access control layer is used to re-verify identity.
In the process isolation layer we also have a range of options. The simplest being application containers. Somewhere in the middle we’d have VDI. Finally we’d have dedicated RAM with remote attestation.
In essence, the policy framework helps you organize a wide range of security controls into three primary categories. Similar to the DIY cyber threat assessment, this model forces us to think thru tradeoffs.
Putting theses different ideas together, we’ll take the different risk groups that we identified in the cyber threat assessment and overlay them onto our 3 tier security control framework. Don’t worry where the lines initially sit. In fact the point of this exercise is to move them around and consider the tradeoff between security and cost for each group.
For high-risk groups such as Finance, utilizing all the security controls makes sense. Similarly supply chain partners accessing an external SaaS may not require too much security. The interesting parts is where all of the other risk groups are placed.
The great thing about this simple policy framework is that it exposes bad ideas really quickly. For example when people want all the security controls turned on for a specific group the difficulty of aligning lots of security controls (i.e. products) becomes pretty apparent. On the positive side, this framework shifts the focus away from buying boxes to managing risk. We’re forced to not just think about policies but the inputs themselves. For example, perhaps the DIY cyber threat assessment was incorrect.


